On Page Optimisation For Beginners
Let us start by explaining what on page optimisation actually is. On page optimisation is optimising your websites pages, more specifically behind the scenes where it can only be seen in your website’s CMS. A CMS is the system you use to build your website, the most popular of all of them being WordPress, followed by Joomla. You want your page to look good to not only your adoring customers/readers but also to the head honcho, Google.
But where do you start? What are you looking out for? Well below as the different subjects we’ll be covering within the on page process:
- Keywords – which ones you should include and how to include them.
- Page Observation – is the website user friendly?
- Title Tags & Meta Descriptions – these are what appear in your Google listing.
- Page Text – there is such a thing as too much, and too little.
- Header Tags – why they’re just as important as meta data.
- Images – do you own the rights to them?
- Crossed and Outbound Links – building up trust through links.
- Page Load Speed – are you a cheetah or a turtle?
- Visibility – stopping duplicate content in its tracks
- Legal Compliance – getting all the information you need.
Photo credit: Pixabay
So, now you know what we’re covering, let’s crack on with the learning!
Keywords
These are the words people use to search for your website, for example if you were looking for a UK wedding blog the keywords would either be “UK wedding blog” or “wedding blog”. Selecting your keywords is not as easy as just picking out what you believe will be the best for your site.
A keyword like “wedding blog” is bound to be a very searched term, however it also makes it an extremely competitive keyword. Remember you’re not the only person who will be using that keyword, higher authority websites will use them and push your listing down. You want to be near the top right? Well the best way to do that is to pick out relevant and perhaps longer tailed keywords that are less competitive.
You can use the Google Keyword Planner to help you work out what keywords work best for you. You can also read this very helpful article by Backlinko on how to carefully choose your keywords and use the keyword planner.
You should be picking out relevant keywords for each of your websites pages with the aim of having around 5 to 10 for each page. You don’t want to bombard your site with the same keyword, but you equally don’t want to have such an array of keywords that they all get lost within your text and CMS.
When I say relevant, I mean keywords that explain the page. You can’t have the keyword “wedding dress” for a page about wedding flowers, for example, as Google will see that it’s not relevant and can penalize you for it. You can also be penalized for overusing or cramming in too many keywords. The aim is to have them flow perfectly within your text so that it sounds natural rather than forced in.
Photo credit: Google Adwords Keyword Planner
Page Observation
Basically just have a play around with the website in question, ask yourself all the questions you think that visitors to your website will be asking. You want to make sure that the page works well and is easy to navigate, not hiding anything from the user. You want your more popular pages to be more prominent on the page and you also want your contact pages to be clear and concise.
If you come across something that could be an issue, but you’re not totally sure, you can always use Usability Hub to test aspects of your website. It’s a fantastic site you can use to test not only designs but also test actions the average user takes when given a simple instruction. You could also just ask a few people to go on the site and give it a once over, from a customer/user point of view. It’s worth testing these aspects of your website as they’re what help to keep people on your website, you need that hook.
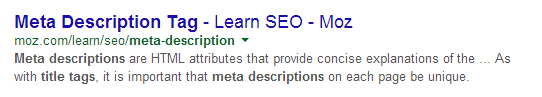
Title Tags & Meta Descriptions
As I said in the introduction, this is what you see on your Google listing. Here is an example of what you’ll see and I’ll tell you which is the title tag and which is the meta description:
Now the title tag here is the line in blue, this needs to be as descriptive as it can possibly be as this is what most people are looking for. Ideally your title tag needs to be 60 – 65 characters long, too little wouldn’t be very descriptive but any more and it’ll get cut off. It should include 1 or 2 primary keywords in, as you can see in the description below, the keywords have been highlighted.
Photo credit: G-Biosciences
The description below the link is the meta description, which is used to further explain what is on the page it’s linking to. This can be any number of words up to 160 characters, any more and it will cut off the rest of your description. This should also include one or two naturally added keywords related to that page. Both the title tag and meta description should read like a sentence, if it doesn’t make much sense then the chances are nobody is going to click on it.
Page Text
Now we move onto the actual text on your website, otherwise known as the page text. You want to make sure that every page has some text on it of around 100 – 200 words, this is so you can add extra keywords but also shows Google that you’re not a blank website. Google absolutely loves content, having a blog, for example, is an absolute must these days as it really helps to build up the strength of your site.
The text needs to be of course relevant to the page, for pages such as a contact form or a blog page with no introduction this isn’t as important as Google can recognise these pages and knows it has no real need for masses of text. You want to make sure you’re not cramming in too many keywords, to test the keyword density of your text you can use SEO Books Keyword Density tool. You want the percentage of each keyword to be below 1.5%, any more and you’re using the keyword too much.
You also need all page text to be unique, duplicate content can get you into some serious trouble and can end in the penalisation of your site. To avoid this you need to firstly write all the content yourself and secondly use Copyscape (or a similar duplicate content checking tool) to make sure you’re content is 100% unique. You are allowed to quote other websites, but don’t let a whole page be quoted text. As long as you’re using quotation marks in the right places you are good to go.
Header Tags
Header tags are very simple, they are the “tags” given to your headers. They vary from a H1 tag to a H6 tag, what’s the difference? Size really. A H1 is the largest in text size, but you don’t choose your header tags because of the size of the text. You choose your header tags quite simply by numbering all your headers. You start with a H1 then work your way up, showing a lovely H1 in all it’s glory.
If we wanted to add another header after the text, we’d then add a H2, then a H3 after that (although you can use more than 1 H2 tag, you can’t use more than one H1 tag realistically). Always make sure that your first header is a H1, also avoid making images such as logos header tags.
You headers need to be between 15 and 60 words long, you’re not trying to create sentences here but you also don’t want headers as basic as one word (nobody likes getting one word answers, right?). The header is there to introduce the content below it, so make it relevant and if possible add in a primary keyword. If you have a keyword in your H1 then try to avoid adding another one in your H2, using lots of keywords in your headers draws too much attention.
Images
Images on your website are great, they can really help to make a website look inviting. However many people make the mistake from just Googling images and just copying and pasting whatever they find. Image usage rights are very strict, using an image without permission is frowned upon and you could see yourself being sued. Make sure you own the images you use on your website or at the very least have the permission to post them. You can use image libraries (that provide stock images) such as iStock, Shutterstock or Dreamstime to pay for the use of images.
Photo credit: iStock
You can alternatively leave credits to the images under the images themselves, linking to the original source. This is not the best way to go as you’ve no proof that the website you found an image on had the right to post the image themselves. You should ideally have at least one image on each of your websites pages that is highly relevant, it again helps to boost your page.
Once you’ve got your image or images you need to optimise them, you can do this by making sure they have alt tags. Alt tags are kind of like a title tag in the sense that it’s describing the image. You can use keywords in here, but only if they accurately describe the image. For example, if you have an image of a cup of coffee you would have the alt tag as “cup of coffee”, you can’t use the keyword “coffee suppliers” as it doesn’t really describe the image itself. Also the title of the images need to ideally share the alt text, rather than the images file name.
Crossed and Outbound Links
Cross linking is linking to other pages on your website and outbound links are any links that go to websites other than your own. It is important to have crossed links so that you’re always showing visitors what you have to offer and make it easier for them to navigate through your website.
Your homepage, for example, should pretty much link to every other main page you have. Your navigation bar will link to all your pages, but crossed links are ones found within the page text on your website. Also try to use keywords as your anchor text where possible for main pages – anchor text being the text shown where a link is.
Outbound links are not as important, but are extremely helpful and can really help to boost your pages visibility and also it’s online presence. These can be links to social pages such as Facebook, Twitter, Google+, LinkedIn or YouTube or they can be links to trusted websites that you either work with/for or have listings/content on. Any awards you may have won should also be linked to either with an image or in a list of achievements.
Photo credit: Flickr
Page Load Speed
You might wonder why this is important, well a pages load speed can deter people from revisiting your website. Slow page load speeds can be tedious and 74% of consumers will wait only up to 5 seconds before leaving a website. You can check your pages load speed using Google’s PageSpeed Insights, ranking your website out of 100 on desktop and on mobile.
It’s an awesome tool that shows you not just how fast/slow your page is running but also shows developers exactly what could be causing the slower speeds. This means it’s done all the work for you, all you need to do is implement the changes to make your speeds better. You’ll need to test every single page on your website, not just the homepage.
Visibility
Homepage visibility is how your web addresses can be seen, for example websites can sometimes be seen as http://www.thissite.com, www.thissite.com, thissite.com or thissite.com/index.php. Having your website seen in several formats like this is not good at all for SEO, it can create duplicate content as Google sees them all as separate websites. Make sure all your URL’s are directed to one location, the most popular choice is www.thissite.com.
Legal Compliance
You may not know it, but every website legally needs to have a contact page, a privacy policy and cookies page. Without them you can be penalised by Google, so you need to get one up and running as soon as you can. It’s super easy to add a contact page to your website, just ask your developer to add one if you don’t already have one. You can also get a free privacy policy and cookies page template from ourselves, just click here to download it.
And there we have it, a basic guide to on page optimisation! Now you can make sure your page is quick, easy to use and compliant.